Maintenance is a critical aspect of managing machinery and infrastructure, and it plays a pivotal role in maximizing Return on Investment (ROI). As businesses strive to optimize their assets, the choice of maintenance strategy becomes paramount. In this era of digital transformation, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is revolutionizing the maintenance landscape, enabling proactive measures to extend the lifespan of machines and reduce downtime. In this blog post, we explore how Industrial Internet of Things is reshaping maintenance strategies, optimizing processes, and ensuring a robust ROI.
What is Proactive Maintenance?
Proactive maintenance is a comprehensive strategy aimed at actively preventing breakdowns before they occur, in stark contrast to reactive maintenance, which addresses issues after they happen. The key to proactive maintenance lies in extending the Potential Failure (P) to Functional Failure (F) interval beyond what is achievable with reactive approaches. This approach is preparation-based, systematically increasing the life expectancy of infrastructure and machinery, thereby reducing maintenance costs and increasing overall operational efficiency.
Comparing Proactive with Reactive Maintenance:
Proactive maintenance differs significantly from reactive strategies. While reactive maintenance is responsive to breakdowns, often resulting in longer downtime, proactive maintenance is structured and organized. It ensures faster response times, shorter repair periods, and overall reduces the expensive impact of unplanned downtime, thereby increasing customer satisfaction.
Proactive Maintenance Strategies:
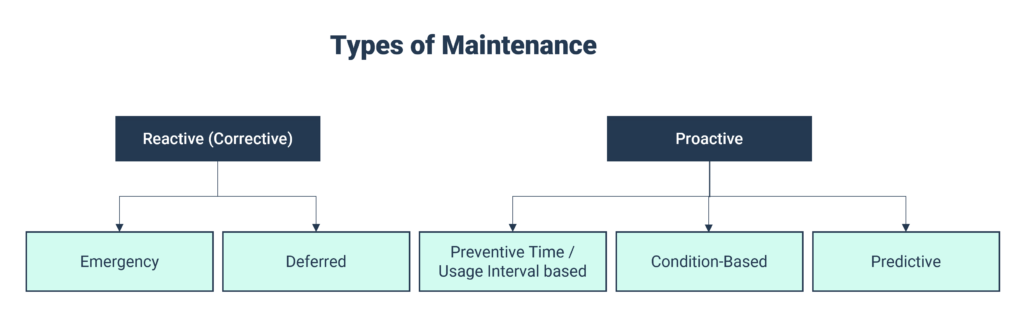
Proactive maintenance comprises three main types:
- Time or Usage Interval-Based Preventative Maintenance: Also referred to Planned Maintenance, this involves regular scheduled inspections, cleaning, upkeep, and periodic part changes to prevent failures.
- Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM): It includes both manual detection methods such as appearance, noise, and smell, as well as digital real-time monitoring using sensors for parameters like temperature, vibration, performance, and pressure.
- Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, predictive maintenance identifies patterns in real-time machine data, allowing for the prediction of potential failures.
Enabling Proactive Maintenance with IIoT:
The advent of IIoT technologies plays a pivotal role in enabling proactive maintenance. Through the digitalization of planned maintenance and CBM, organizations can now monitor, analyze, and act on machine data in real-time. This digital transformation empowers maintenance teams to stay ahead of potential issues, reducing the risk of unplanned downtime.
Examples of IIoT Supported Maintenance:
- IIoT-Supported Planned Maintenance: Imagine a production line where sensors digitally count the number of cycles a machine completes. Once a predefined threshold is reached, an in-app task notification is sent to the maintenance team, prompting them to conduct a proactive inspection.
- IIoT-Supported Condition-Based Maintenance: Temperature sensors on a production line detect an increase in heat from a machine, surpassing a set threshold. An in-app task notification is sent to the relevant team member, who, having experienced this before, knows the required part and replaces it during a scheduled production line changeover, preventing an unplanned breakdown.
Reassessing Maintenance Strategies:
With the new possibilities offered by IIoT, it becomes imperative to reassess existing maintenance strategies. However, a one-size-fits-all approach should be avoided. Identifying maintenance scenarios and prioritizing the most significant risks is crucial. Innius’ Downtime report, utilizing Pareto analysis, can be a valuable tool for comparing downtime reasons with their impact. It’s then important to calculate the business case to see which maintenance strategy will deliver the ROI compared to the potential financial risk of machine failure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the fusion of proactive maintenance and IIoT is reshaping the industrial landscape. By leveraging digitalization, organizations can enhance their maintenance strategies, reduce downtime, and ultimately boost their profits. The combination of digital Condition-Based Monitoring and planned maintenance, supported by IIoT technologies, such as innius, offers a promising future for industries looking to stay ahead in the competitive market. As we embrace the era of Industry 4.0, proactive maintenance with IIoT is not just a strategy but a necessity for sustainable success.